Saturday, December 27, 2008
Definitions - Fiscal Policy
IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS FROM CHAPTER 10
Fiscal policy refers to taxing and spending by the government.
Aggregate demand (AD) is overall spending on newly produced goods and services. It is composed of consumption (C), investment (I), government purchases (G), and net exports (X-M).
Expansionary fiscal policy attempts to stimulate the economy by increasing overall spending on newly produced goods and services through (1) increased government purchases (G), or (2) decreased taxes to encourage more consumption (C) and investment (I) spending. Expansionary fiscal policy can be used to fight unemployment. It also promotes economic growth if it generates investment in physical capital, human capital, and technology, which tend to increase productivity.
Contractionary fiscal policy attempts to slow the economy by decreasing overall spending on newly produced goods and services through (1) decreased government purchases, or (2) increased taxes to discourage consumption and investment spending. Contractionary fiscal policy can be used to fight inflation.
Fiscal policy’s political bias is that politicians are reluctant to conduct contractionary fiscal policy because increasing taxes and reducing government spending on constituents are politically unpopular.
The efficiency of a tax system refers to the relative costs it imposes on taxpayers beyond the monetary payments from taxpayers to the government. These costs include the effect on incentives and behavior and the administrative burden of complying with the tax laws.
The marginal tax rate is the tax paid on an additional dollar of income.
The opportunity cost is what is sacrificed or foregone when a choice is made.
Standard of living measures the amount of goods and services consumed by an average person.
Quality of life attempts to measure the fulfillment people receive.
The equity of a tax system concerns whether the tax burden is distributed fairly among the population.
Vertical equity is the idea that taxpayers with a greater ability to pay taxes should pay larger amounts.
Horizontal equity is the idea that taxpayers with similar abilities to pay taxes should pay the same amount.
The benefits principle states it is fair for people to pay taxes based on the benefits they receive from the government.
The ability-to-pay-principle states it is fair for people to pay taxes based on their capability to handle the financial burden.
A progressive tax is a tax for which high-income taxpayers pay a larger percentage of their income than do low-income taxpayers.
A proportional tax is a tax for which high-income and low-income taxpayers pay the same percentage of income.
A regressive tax is a tax for which high-income taxpayers pay a smaller percentage of their income than do low-income taxpayers.
The average tax rate is the total taxes paid divided by total income.
The marginal tax rate is the tax paid on an additional dollar of income.
A lump-sum tax is a tax that is the same monetary amount for every person.
A flat tax is a tax in which every taxpayer is subject to the same marginal tax rate.
Vertical equity is the principle that taxpayers with a greater ability to pay taxes should pay larger amounts.
Social Security is a government program that imposes taxes on wage earners and employers, and provides old-age, survivors’, disability, and medical benefits to workers covered under the Social Security Act.
A transfer payment is a government payment not made in exchange for a good or service.
National defense includes both the salaries of military personnel and the purchases of military equipment, such as guns, fighter jets, and warships.
Income security includes transfer payments to poor families.
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) is a government social program that transfers income from taxpayers to poor families.
The food stamp program is a government social program that gives poor families vouchers that they can use to buy food.
Net interest is the amount the government pays on loans from the public.
Medicare is the federal government’s social program that provides health care benefits to the elderly.
Medicaid is the federal government’s social program that provides health care benefits to the poor.
The U.S. federal budget balance is the difference between U.S. government revenues and U.S. government expenditures.
A budget surplus is an excess of government receipts over government spending.
A budget deficit is an excess of government spending over government receipts.
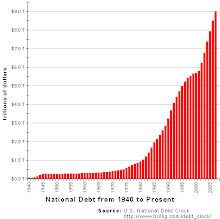
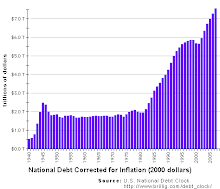
The public debt is the accumulation of deficits and surpluses over time.
Fiscal policy refers to taxing and spending by the government.
Aggregate demand (AD) is overall spending on newly produced goods and services. It is composed of consumption (C), investment (I), government purchases (G), and net exports (X-M).
Expansionary fiscal policy attempts to stimulate the economy by increasing overall spending on newly produced goods and services through (1) increased government purchases (G), or (2) decreased taxes to encourage more consumption (C) and investment (I) spending. Expansionary fiscal policy can be used to fight unemployment. It also promotes economic growth if it generates investment in physical capital, human capital, and technology, which tend to increase productivity.
Contractionary fiscal policy attempts to slow the economy by decreasing overall spending on newly produced goods and services through (1) decreased government purchases, or (2) increased taxes to discourage consumption and investment spending. Contractionary fiscal policy can be used to fight inflation.
Fiscal policy’s political bias is that politicians are reluctant to conduct contractionary fiscal policy because increasing taxes and reducing government spending on constituents are politically unpopular.
The efficiency of a tax system refers to the relative costs it imposes on taxpayers beyond the monetary payments from taxpayers to the government. These costs include the effect on incentives and behavior and the administrative burden of complying with the tax laws.
The marginal tax rate is the tax paid on an additional dollar of income.
The opportunity cost is what is sacrificed or foregone when a choice is made.
Standard of living measures the amount of goods and services consumed by an average person.
Quality of life attempts to measure the fulfillment people receive.
The equity of a tax system concerns whether the tax burden is distributed fairly among the population.
Vertical equity is the idea that taxpayers with a greater ability to pay taxes should pay larger amounts.
Horizontal equity is the idea that taxpayers with similar abilities to pay taxes should pay the same amount.
The benefits principle states it is fair for people to pay taxes based on the benefits they receive from the government.
The ability-to-pay-principle states it is fair for people to pay taxes based on their capability to handle the financial burden.
A progressive tax is a tax for which high-income taxpayers pay a larger percentage of their income than do low-income taxpayers.
A proportional tax is a tax for which high-income and low-income taxpayers pay the same percentage of income.
A regressive tax is a tax for which high-income taxpayers pay a smaller percentage of their income than do low-income taxpayers.
The average tax rate is the total taxes paid divided by total income.
The marginal tax rate is the tax paid on an additional dollar of income.
A lump-sum tax is a tax that is the same monetary amount for every person.
A flat tax is a tax in which every taxpayer is subject to the same marginal tax rate.
Vertical equity is the principle that taxpayers with a greater ability to pay taxes should pay larger amounts.
Social Security is a government program that imposes taxes on wage earners and employers, and provides old-age, survivors’, disability, and medical benefits to workers covered under the Social Security Act.
A transfer payment is a government payment not made in exchange for a good or service.
National defense includes both the salaries of military personnel and the purchases of military equipment, such as guns, fighter jets, and warships.
Income security includes transfer payments to poor families.
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) is a government social program that transfers income from taxpayers to poor families.
The food stamp program is a government social program that gives poor families vouchers that they can use to buy food.
Net interest is the amount the government pays on loans from the public.
Medicare is the federal government’s social program that provides health care benefits to the elderly.
Medicaid is the federal government’s social program that provides health care benefits to the poor.
The U.S. federal budget balance is the difference between U.S. government revenues and U.S. government expenditures.
A budget surplus is an excess of government receipts over government spending.
A budget deficit is an excess of government spending over government receipts.
The public debt is the accumulation of deficits and surpluses over time.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)




Excellent policy
ReplyDelete